Natal Indian Congress
Enlarge text Shrink text- 90 fighting years 1894-1984, Natal Indian Congress, Gandhi -Dadoo -Naicker - Sewpersadh ..., 1984:
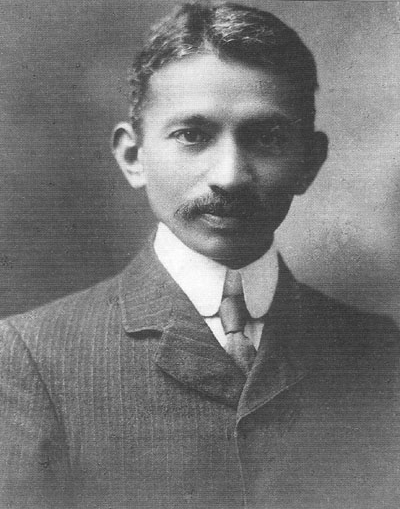
The Natal Indian Congress (NIC) was a political organisation established in 1894 to fight discrimination against Indians in the Natal Colony, and later the Natal Province, of South Africa. Founded by Mahatma Gandhi, it later served an important role in opposing apartheid. It was the oldest affiliate of the South African Indian Congress. During its formative years, the constituency of the NIC largely comprised educated Indian merchants who sought to oppose discriminatory legislation through petitioning. In the mid-1940s, the organisation became increasing confrontational under the leadership of Monty Naicker, who led the NIC through a renowned campaign of passive resistance against the Asiatic Land Tenure and Indian Representation Act from 1946 to 1948. After the introduction of formal apartheid in 1948, the NIC participated in the Defiance Campaign, the beginning of a long, though not untroubled, alliance with the African National Congress (ANC). In the 1960s, members of the NIC and other Congress Alliance organisations faced increased state repression, and the organisation entered a decade of dormancy. It was revived in October 1971 and continued its activism against apartheid, notably through boycotts of the South African Indian Council and Tricameral Parliament. The NIC was a founding affiliate of the United Democratic Front, whose leadership often overlapped with that of the NIC. Although the NIC was represented at the Convention for a Democratic South Africa in 1991, it did not restructure itself as a political party during South Africa's democratic transition. Instead, many leaders and members joined the ANC, and the NIC again fell into dormancy from around the time of the first post-apartheid elections in 1994.
Read more on Wikipedia >
 Corporate Body
Corporate Body