Intestinal mucosa
Enlarge text Shrink text- Work cat.: The mucosal immune system, 1981.
- MESH.
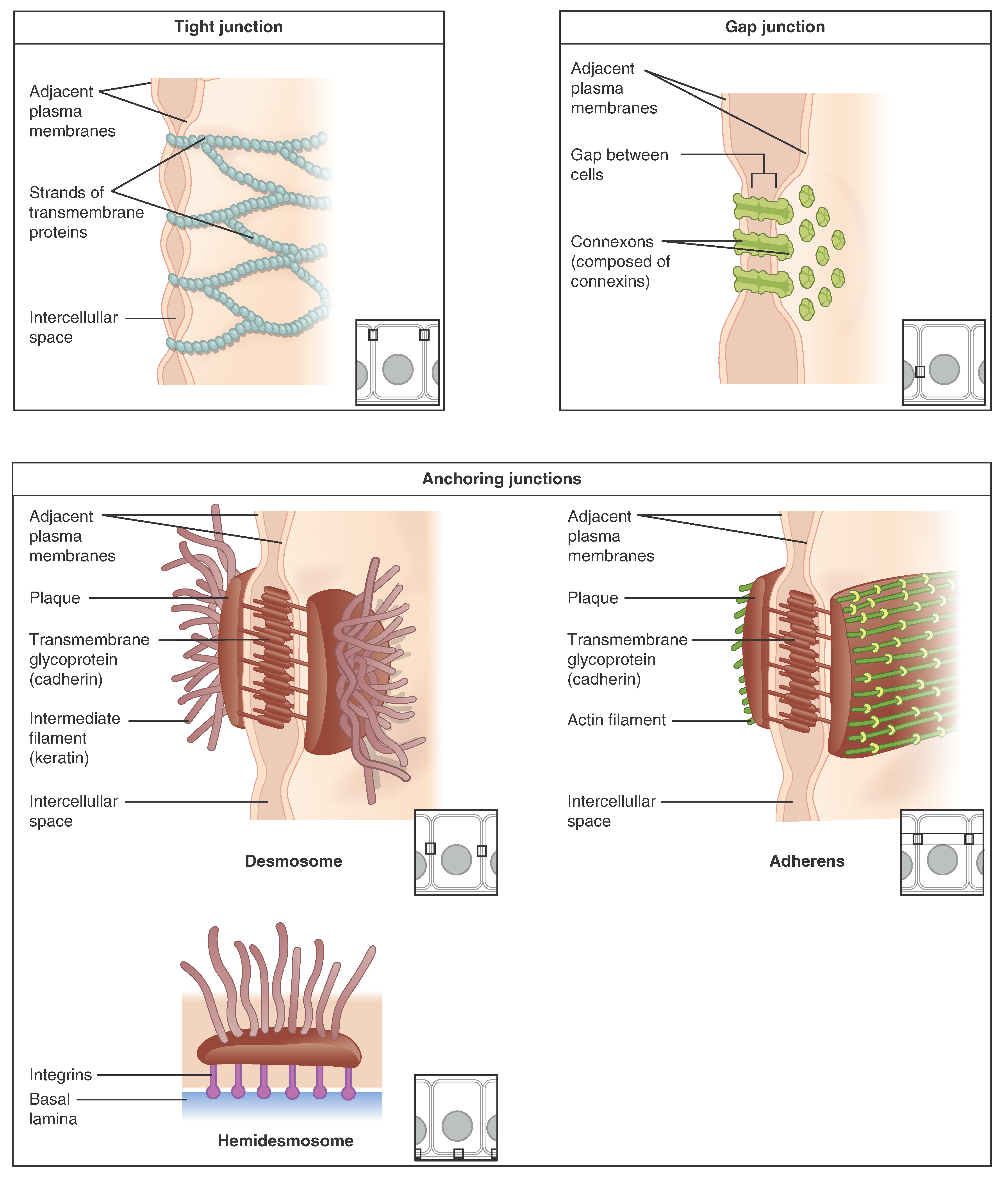
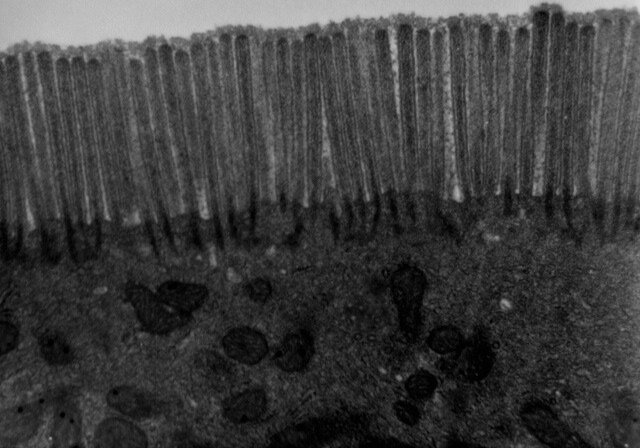
The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that forms the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract. Composed of simple columnar epithelium its main functions are absorption, and secretion. Useful substances are absorbed into the body, and the entry of harmful substances is restricted. Secretions include mucins, and peptides. Absorptive cells in the small intestine are known as enterocytes, and in the colon they are known as colonocytes. The other cell types are the secretory cells – goblet cells, Paneth cells, enteroendocrine cells, and Tuft cells. Paneth cells are absent in the colon. As part of its protective role, the intestinal epithelium forms an important component of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Certain diseases and conditions are caused by functional defects in the intestinal epithelium. On the other hand, various diseases and conditions can lead to its dysfunction which, in turn, can lead to further complications.
Read more on Wikipedia >
 Topic
Topic