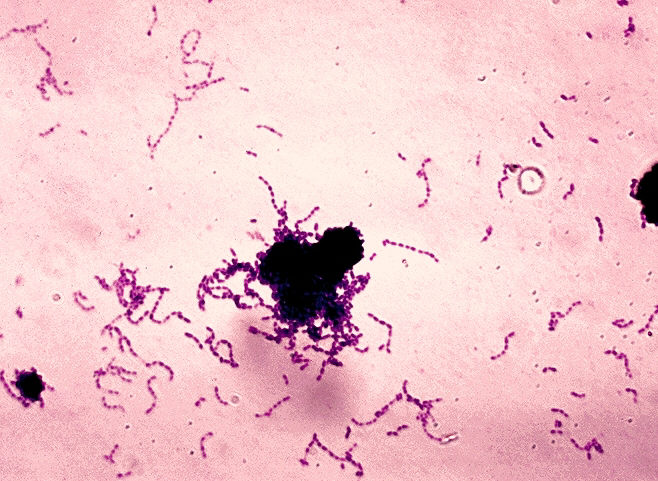
Streptococcus mutans
Enlarge text Shrink textStreptococcus mutans is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. The microbe was first described by James Kilian Clarke in 1924. This bacterium, along with the closely related species Streptococcus sobrinus, can cohabit the mouth: Both contribute to oral disease, and the expense of differentiating them in laboratory testing is often not clinically necessary. Therefore, for clinical purposes they are often considered together as a group, called the mutans streptococci. This grouping of similar bacteria with similar tropism can also be seen in the viridans streptococci – which Streptococcus mutans is itself also a member of.
Read more on Wikipedia >
 Topic
Topic